According to the WHO, every year every second person on the planet is infected with helminths. Many people think that parasitic worms are not very harmful to health. However, not everything is so simple: helminths are capable of infecting important internal organs: the heart, lungs, and the brain.
Helminths - who are they?
Helminths are parasitic worms that can choose the body of a person, animal, plant as a host. There are three classes of helminths in total:
- tapeworms.This class includes about 3. 5 thousand types of helminths. The length of parasitic worms varies from a few mm to 10-15 meters;
- flukes.Parasites got their name due to the presence of suckers in them, with the help of which they receive nutrients. The human body can infect about 4 dozen species of flukes. As a rule, the length of the worms does not exceed 5 cm;
- round worms.This class of helminths has more than 24 thousand species. Roundworms are spindle-shaped. Usually their length is no more than 0. 5 meters.
You can become infected with helminths in various ways. However, most often parasitic invasion occurs for the following reasons:
- Poor hand hygiene.
- Unwashed vegetables, fruits; undercooked or undercooked meat, fish - the use of such products increases the risk of parasitic infestation many times over.
- Keeping food open outside the refrigerator. Insects are capable of transferring helminth eggs to foods that are stored without packaging.
- Contact with pets.

The main symptoms of the presence of parasites in the body:
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- weight loss;
- allergic rashes;
- bloating;
- itching in the anus;
- grinding teeth in a dream.
What helminths are most common in Russia? Consider the most common types of parasitic worms and the diseases they cause.
Tapeworms
The body of the tapeworm consists of members, the total number of which ranges from 3 to 5000. The main element of fixation of the helminth is the head, additional ones are suction cups, hooks.
The most common causes of tapeworms are:
- diphyllobothriasis;
- teniarinhoses;
- teniasis.
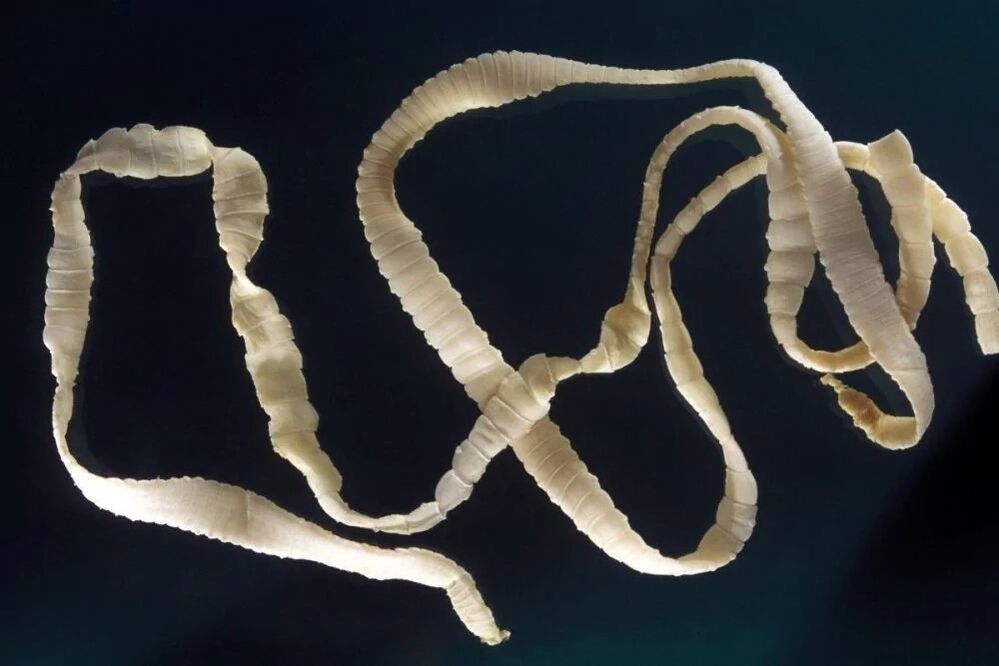
Diphyllobothriasis
The causative agent of the disease is a broad tapeworm that affects the human intestine. The development of worm eggs occurs in fresh water. The scheme of the tapeworm entering the human body is as follows:
- The eggs of the worm are swallowed by crustaceans that live in the reservoir.
- Infected crustaceans are eaten by fish.
- A person becomes infected with a parasite by eating fish that has undergone insufficient heat treatment.
The symptomatology of the disease develops 1. 5 months after infection. The main sign of pathology is the presence of whitish fragments of helminth in the feces.
Attaching to the intestinal mucosa, the tapeworm absorbs a large amount of vitamin B12. For this reason, people with diphyllobothriasis often develop anemia. In addition, the tapeworm can cause an increase in the liver, spleen, intestinal obstruction.
Teniarinhoz
The causative agent of the disease is bovine tapeworm, which predominantly lives in the human small intestine. During its development cycle, the helminth replaces two hosts: the intermediate is cattle, the main one is man. Bovine tapeworm can live in the body for 20 years, multiplying and causing harm to health.
Typically, people develop teniarinhoses after eating undercooked or undercooked beef.
The disease often proceeds without pronounced symptoms and is detected by chance when a person sees elements of helminth in his feces. In some people, in addition to the main signs of infection with helminths, pain syndrome may occur in the right side of the anterior abdominal wall.
Adult helminths are able to penetrate the appendix, pancreatic duct, biliary tract, provoking acute inflammatory processes in them. With multiple parasitic infestations, intestinal obstruction may develop.
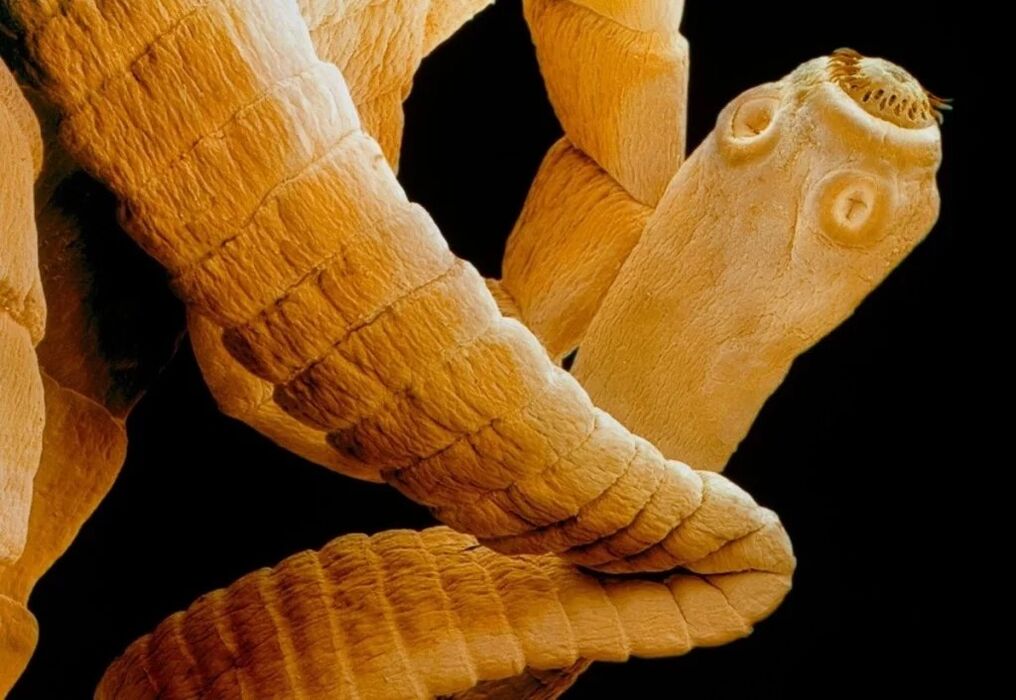

Teniosis
The causative agent of the disease is pork tapeworm, which initially affects the human small intestine. Human infection occurs through the consumption of raw or improperly cooked pork.
The parasite can penetrate into various organs and tissues, causing pain in the abdomen, back, limbs. The pathology is most favorable when the worm is localized in the subcutaneous fat and skeletal muscle tissue. When worms penetrate into the eye muscles, they cause a decrease in visual acuity, lacrimation, and photophobia. The defeat of the pork chain of the brain can be fatal.
Suckers
Flukes are leaf-shaped and have a high ability to reproduce at different periods of the life cycle. Reproduction of worms is possible not only sexually with fertilization, but also without it. In addition to suckers, worms have many hooks and spines, due to which they reliably attach to the mucous membranes of organs.
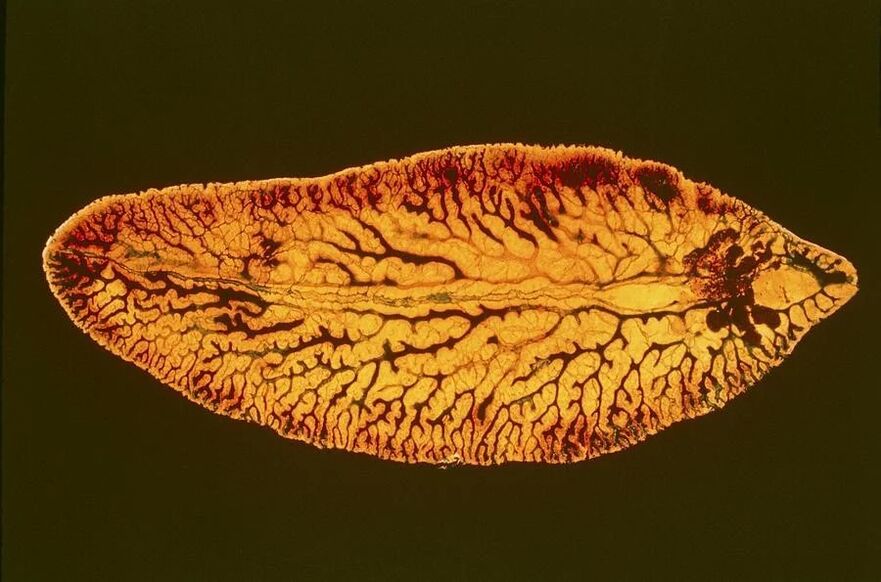
Common pathologies caused by flukes:
- fascioliasis;
- opisthorchiasis;
- paragonimiasis.
Fascioliasis
Fascioliasis occurs when the liver or gallbladder is damaged by the hepatic fluke. Basically, infection occurs when eating vegetables, for which water was used from open reservoirs.
In addition to the standard signs of parasite infection, a person may experience asthmatic attacks, which are accompanied by shortness of breath, facial flushing, dilated pupils, and tachycardia. If an adult has caused obstruction of the bile ducts, then obstructive jaundice develops. Signs of pathology:
- cramping pain in the right hypochondrium;
- yellowing of the skin;
- fever;
- colorless feces.
Opisthorchiasis
The causative agent of the disease is a feline fluke. The name of the parasite is due to the fact that, in addition to humans, it often infects cats and other mammals that eat fish.
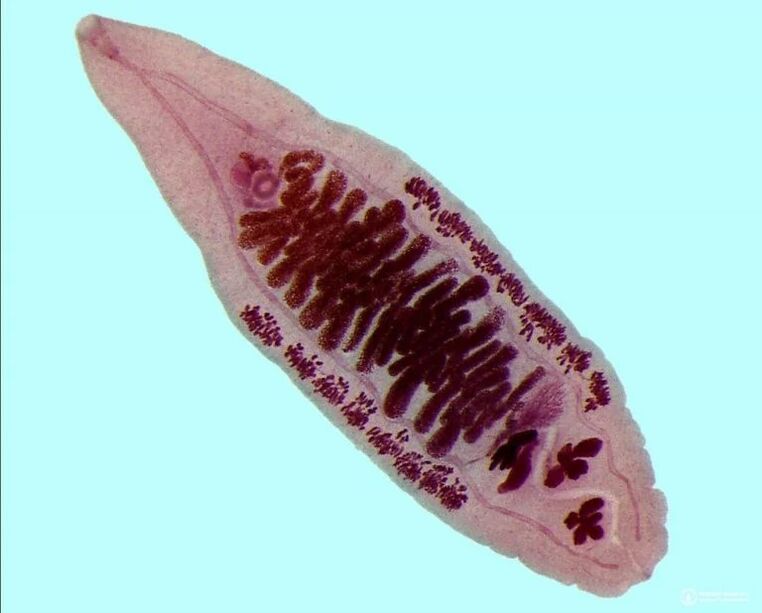
As a rule, the feline fluke affects the liver and pancreas, causing inflammation in the organs. Symptoms are varied and depend on the number of parasites. The patient may experience:
- symptoms of intoxication;
- fever;
- hives;
- itchy skin;
- pain in muscles, joints, right hypochondrium.
In some cases, helminths cause an increase in lymph nodes, the development of jaundice. The chronic form of pathology often leads to hepatitis, liver cirrhosis.
Paragonimiasis
The culprit of the disease is a pulmonary fluke, which enters the human body with infected crustaceans.
First, the parasite enters the human intestine, then into the abdominal cavity. The end point of his journey is lung tissue. In addition, the worm is able to penetrate the brain and affect the central nervous system.
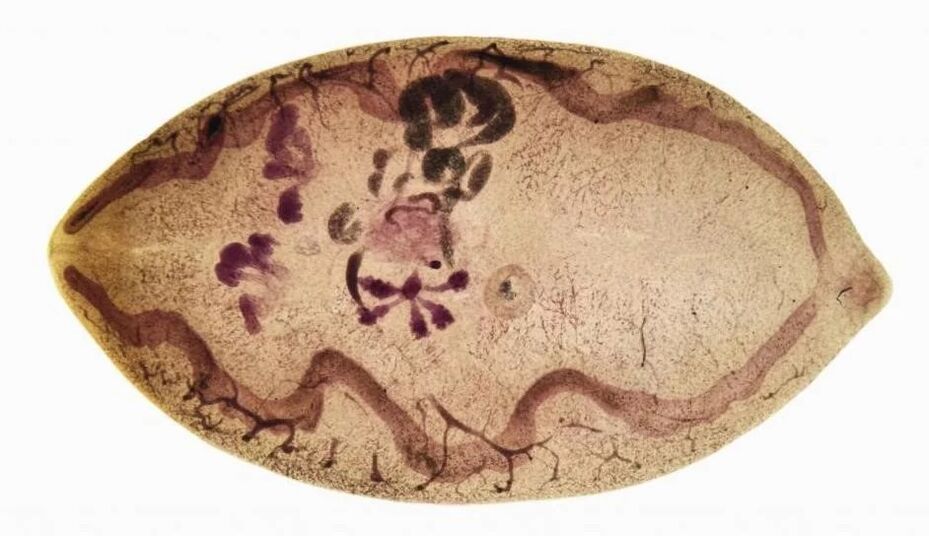
Specific signs of parasitic invasion of the lungs:
- pain in the chest;
- cough with phlegm, which may contain pus and blood;
- fever.
In some cases, helminths cause a violation of the ventilation function of the lungs and gas exchange during breathing.
Round worms
Due to their structure, roundworms (nematodes) are able to survive even in extreme conditions. Their body is covered with a three-layer musculocutaneous sac, which reliably protects parasites from external influences.
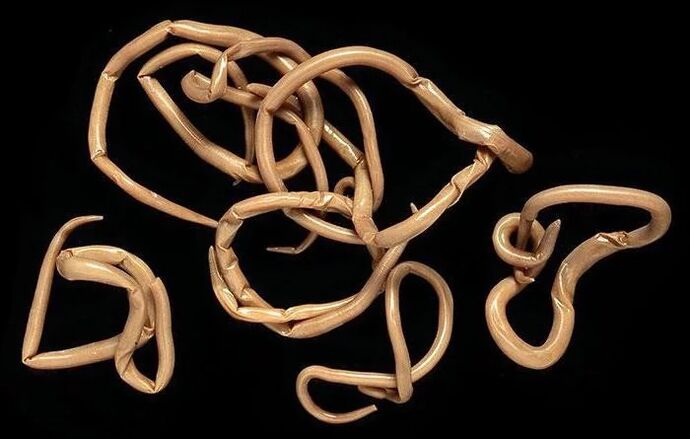

Common diseases caused by nematodes:
- ascariasis;
- enterobiasis;
- trichinosis.
Ascariasis
The development of the disease provokes ascaris, which is initially fixed in the small intestine. The average length of adults is 40 cm. The larvae of the parasite can enter the human digestive system with unwashed vegetables and fruits, contaminated water. Also, poorly washed hands before eating are often the cause of ascariasis.
During the penetration of the larvae into the human body, a subfebrile temperature, allergic rashes, cough with the release of transparent sputum can be observed. Signs of the intestinal stage of ascariasis (diarrhea, abdominal pain) are observed only in the presence of several parasites. As a rule, living in the intestines of one worm is asymptomatic.
Complications with multiple parasitic infestations:
- blockage of the bile duct;
- purulent inflammatory processes in the gallbladder, liver;
- inflammation of the appendix;
- intestinal obstruction.
Enterobiasis
The provocateurs of the disease are pinworms - small worms up to 1 cm long. Helminths penetrate the human digestive system in the same way as roundworms.

Currently, enterobiasis is the most common parasitic pathology in the world. Basically, the disease is diagnosed in children under the age of 10.
Symptoms, as in previous cases, develop only with multiple parasitic infestations. Children often have diarrhea, mucus in the stool, difficult and painful digestion, itching in the anus, and nausea. With a severe course of the disease, limb cramps may occur. In addition, pinworms are able to penetrate the genitals, causing acute inflammation in them.
Trichinosis
This disease provokes Trichinella - one of the smallest parasitic worms. The length of the parasite rarely exceeds 4 mm. In the larval stage, worms can infect skeletal muscles. The exception is the myocardium - the muscle tissue of the heart. Adults parasitize in the small intestine.
As a rule, human infection occurs when eating half-baked pork. At the same time, for the development of the disease, it is enough to consume only 30 g of meat affected by parasites.
Pathology is manifested by the standard symptoms of parasitic invasion. In an advanced stage, swelling of the eyelids, face, arms and legs, pain in the lower back, and masticatory muscles may occur. Possible complications are complete or partial loss of mobility, airway paralysis.
How to avoid infection with helminths?
To reduce the risk of becoming infected with parasitic worms, it is important to follow these guidelines:
- Wash hands thoroughly before eating, after visiting the street, public places.
- Observe the correct technology for cooking meat, fish. Heat treatment of meat and fish products should last at least 20 minutes.
- Do not eat dried or dried fish.
- Carry out deworming of pets.
- Get tested regularly, even if you have no pathological signs. The most common diagnostic methods are macroscopic and microscopic examination of feces. The first method allows you to detect adults, the second - eggs and larvae of worms.