One of the large sections of protozoology is devoted to unicellular microorganisms, and considers the protozoan human parasites as one of the forms of existence of organisms.
From the point of view of medical parasitology, which studies the ways and causes of diseases, their symptoms (one of the individual signs, the frequent manifestation of a disease, pathological condition or disturbance of any life process) and methods of treatment, protozoa occupy a leading position. They are followed by helminthology aimed at getting rid of helminthic invasions and arachnoentomology - systemic methods in medicine that get rid of arthropod parasites.
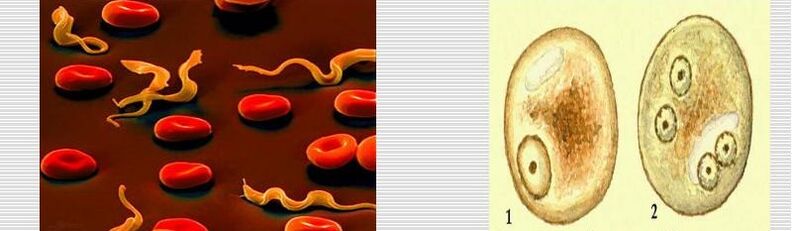
The animal world is represented in abundance by single-celled microorganisms that live everywhere - from the seabed to the upper atmosphere. All of them belong to the sub-kingdom of protozoans, or protozoa, which has more than 15 thousand representatives of unicellular creatures.
Among free-living unicellular species, there are parasitic forms classified as a separate category that cause a number of serious diseases - protozoonoses, and their corresponding symptoms, says a senior researcher at the medical center.
The simplest have several dozen species of parasites that live at the expense of the human body. Amoebas are localized in the intestinal tract, causing symptoms (one of the individual signs, a frequent manifestation of any disease, pathological condition or disturbance of any vital process) amoebiasis. If this is a dysentery form of the parasite, then it provokes the development of dysentery, as well as Giardia, which causes giardiasis. The soft tissues of the internal organs can be affected by Plasmodium and Toxoplasma, causing unpleasant symptoms of toxoplasmosis, requiring specific treatment.
The structure of unicellular organisms
The body of a microorganism is only one cell, which includes the nucleus and cytoplasm. It is lined with a cytoplasmic membrane containing organelles - the endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, the Golgi apparatus and mitochondria. All of them provide the processes of nutrition, respiration, movement, metabolic processes and excretion.
The body of a unicellular organism has both a constant and a changeable shape (it can mean: the shape of an object - the relative position of the boundaries (contours) of the object, object, as well as the relative position of the points of the line). Some representatives of the protozoa have symmetrical bodies, and some have an asymmetric body shape. Representatives of flagellated parasites in appearance resemble a spindle. The rhizomes of the form (it can mean: the shape of the object - the mutual arrangement of the boundaries (contours) of the object, the object, as well as the relative position of the points of the line) do not have a body at all.
Cells divide by simple mitosis, but in some species, in the process of reproduction, fertilization occurs sexually with the formation of a zygote. Almost all the simplest organisms are heterotrophs, but among them there are autotrophic species of unicellular parasites.
The motor function is produced in the amoeba due to the pseudopodia, it seems to overflow, throwing out pseudopodia. Ciliates move due to the often shortening cilia that cover their body in abundance. The movement of the flagella is due to the movement of the flagella themselves, from which they got their unpretentious name.
The amoeba feeding process is also associated with pseudopodia, wrapping food with pseudopodia and absorbing it. Some forms feed using a cellular mouth. Digestion is carried out by phagocytosis - an internal process, as well as by pinocytosis - the process of external absorption of food by the entire surface of the body.
The main feature of protozoa upon the onset of adverse conditions is the formation of cysts. The process of formation of cysts for the dysenteric amoeba is especially characteristic. It allows the parasite (\one of the types of coexistence of organisms) to maintain its vital abilities during a period of prolonged anabiosis.
The main classes of protozoan parasites (one of the types of coexistence of organisms)
Representatives of unicellular organisms (a living body that has a set of properties that distinguish it from inanimate matter, including metabolism, self-maintenance of its structure and organization, and the ability to reproduce them) are assigned to four main classes:
Sarcode class
The sarcode class includes one of the most common, dangerous to humans, unicellular parasite - dysenteric amoeba, which exists in the form of 4 different forms:
- The vegetative form is the largest, reaching 20 microns in size. Finding a parasite in freshly passed stool confirms a disappointing diagnosis, the symptoms of which speak for themselves.
- Tissue, or pathogenic form of the parasite, leading a parasitic lifestyle in the lumen of the colon. The defeat of the amoeba of the intestinal mucosa is produced in a specific way.
- Translucent, or the main form of the dysenteric amoeba that lives in the lumen of the large intestine. This form causes characteristic symptoms for this disease. They are observed in the process of remission of the patient or in the stage of carriage. In the stools of any nature, the presence of the parasite was not established.
- The pre-cystic form of the amoeba is fixed in the semi-formed feces of a human carrier of the disease, or in a patient at the stage of recovery.
The main symptoms of diseases caused by amoebic forms are manifested by permanent sharp pains in the lower abdomen, frequent bowel movements of brown stools due to blood content and streaks of mucus. The body temperature remains within normal limits. A similar picture can periodically accompany the patient for several years and leads to exhaustion, as well as to the development of anemia. With complications caused by the tissue form of the amoeba, and without appropriate treatment, the patient may die.
Class flagellates, or flagellates
A characteristic feature is the equipping of the body with the simplest organs of movement - one or more flagella. Pathogenic widespread microorganisms of this class are:
- trypanosomes, which cause African sleeping sickness;
- leshmania causing urban or rural leishmaniasis;
- trichomonas - causative agents of trichomoniasis, mainly of the vaginal form;
- Giardia is a protozoan that causes giardiasis.
class of sporozoans
Typical representatives of sporozoans are malarial plasmodium, which causes symptoms of valaria and toxoplasma, causing noxoplasmosis.
ciliate class
For microorganisms of this class, a characteristic feature is the presence of cilia throughout the body of the microorganism. They perform a motor function, thanks to which ciliates have the ability to move quickly. The representative of the class is balantidia - the largest human parasite from the protozoan family. Causes a serious and severe disease balantidiasis on the background of the ulcerative process. The disease proceeds in an acute subclinical form, and can be fatal.